Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO)
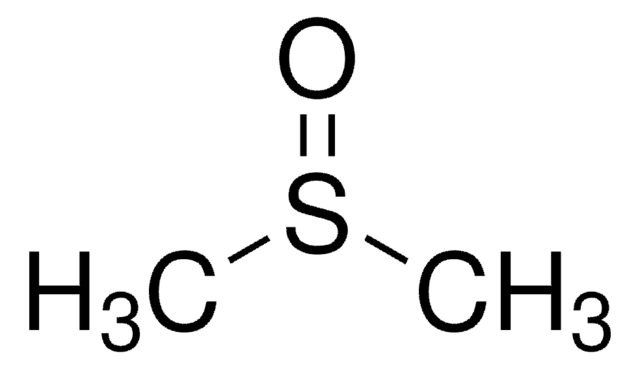
Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) - (CH3)2SO
| Class | Sulfoxides |
| Chemical Formula | (CH3)2SO |
| Molecular Formula | C2H6OS |
| Molecular Weight | 78.13 g/mol |
| Optimal Conc | 5% - 10% (v/v) |
Synonyms
Also Known As
Dimethyl Sulphoxide
Dimethylsulfoxide
Dimethylsulphinyl
Dimexide
DMSO
Rheumabene
Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO)
Is on FDAs GRAS list
Cryoprotectant Use
DMSO is widely used in cryopreservation due to its ability to penetrate cell membranes and prevent ice crystal formation, which can cause cellular damage during the freezing and thawing processes. By lowering the freezing point and increasing the viscosity of the intracellular and extracellular solutions, DMSO helps in reducing the mechanical stresses on cells.
Applications
Cell Preservation: DMSO is used in the cryopreservation of a variety of cell types, including stem cells, blood cells, and sperm cells.
Tissue Preservation: It is used to preserve tissues, such as corneas and skin, for transplantation.
Research: In laboratory settings, DMSO is used to store and preserve cell lines and other biological samples.
Why Use DMSO Instead of Other Cryoprotectants?
Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) is a widely used cryoprotectant due to its unique properties and effectiveness in preserving various types of cells and tissues during the cryopreservation process. Here are several reasons why DMSO is preferred over other cryoprotectants:
1. Penetration Ability
DMSO is a small, polar molecule that can easily penetrate cell membranes. This ability allows it to replace water inside cells, preventing the formation of ice crystals that can damage cell membranes and internal structures. Many other cryoprotectants, such as glycerol, do not penetrate cell membranes as effectively, making DMSO more suitable for certain cell types.
2. Wide Range of Compatibility
DMSO is effective in preserving a wide variety of cells, including stem cells, blood cells, and reproductive cells. Its broad compatibility makes it a versatile cryoprotectant in both research and clinical applications.
3. High Cryoprotective Efficiency
DMSO has been shown to have high cryoprotective efficiency, meaning it is highly effective at preserving the biological function and structure of cells during freezing and thawing processes. This efficiency is crucial for applications where maintaining cell viability is essential, such as in cell therapy and regenerative medicine.
4. Solubility
DMSO is highly soluble in both water and organic solvents. This solubility allows it to be easily mixed with various cryoprotective media, providing flexibility in cryopreservation protocols.
5. Vitrification Ability
DMSO can help cells reach a vitrified state (a glass-like state without ice crystallization) when used in appropriate concentrations and combined with other cryoprotectants. Vitrification is important for preserving delicate cells and tissues that are particularly sensitive to ice formation.
6. Established Protocols
There are well-established protocols for using DMSO in cryopreservation, which have been extensively studied and validated over decades. This extensive body of knowledge provides a reliable framework for researchers and clinicians to follow, reducing the risk of cell damage and increasing the success rate of cryopreservation efforts.
Mechanism of Action
Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) works by replacing water molecules in the cells, thereby preventing the formation of ice crystals that can damage the cell membrane and internal structures. This substitution is crucial during the cooling process, as ice formation within cells can lead to cell death.
Concentration and Protocol
The concentration of DMSO used for cryopreservation typically ranges from 5% to 10% (v/v). The exact concentration and protocol may vary depending on the cell type and specific requirements of the preservation process. Generally, cells are suspended in a cryoprotective medium containing DMSO, cooled slowly to a specific temperature, and then stored in liquid nitrogen.
Safety and Handling
While DMSO is an effective cryoprotectant, it must be handled with care:
Toxicity: DMSO can be toxic at high concentrations and may cause irritation to the skin and eyes.
Handling: Proper personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and safety glasses, should be worn when handling DMSO.
Storage: DMSO should be stored in a cool, dry place away from light and moisture.
Advantages
Penetration: DMSO's ability to penetrate cell membranes makes it highly effective in protecting cells during cryopreservation.
Solubility: It is highly soluble in both water and organic solvents, making it versatile for various applications.
Efficacy: It has been shown to be effective in preserving a wide range of cells and tissues.
Disadvantages
Toxicity: DMSO can be cytotoxic at high concentrations and prolonged exposure.
Side Effects: In some cases, DMSO may cause adverse reactions in the cells being preserved.
Conclusion
Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) is a critical cryoprotectant used in the preservation of cells and tissues. Its effectiveness in preventing ice crystal formation and its ability to penetrate cell membranes make it an invaluable tool in both clinical and research settings. However, its use must be carefully managed due to its potential toxicity and handling requirements.
References
Information
CAS number: 67-68-5
Class | Sulfoxides |
Chemical Formula | (CH3)2SO |
Molecular Formula | C2H6OS |
Molecular Weight | 78.13 g/mol |
Optimal Conc | 5% - 10% (v/v) |
Synonyms
Also Known As
Dimethyl Sulphoxide
Dimethylsulfoxide
Dimethylsulphinyl
Dimexide
DMSO
Rheumabene
Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO)
Is on FDAs GRAS list
